01. Automated Helium Inspection System for Blade Batteries
Multiple factors contribute to battery leaks in new-generation power cells. These encompass pressure, temperature fluctuations, impact vibrations, chemical erosion, welding, and electrolyte infusion, among others.
In the realm of large-scale, high-speed production, the approach to detecting lithium battery leaks directly shapes product safety and performance. Conventional leak detection methods carry notable risks; however, helium leak detection offers a safer and more efficient solution.
This is where the application of helium mass spectrometry leak detectors shines. Employing helium mass spectrometry enables the thorough evaluation of seal integrity of blade batteries, ensuring alignment with designated design standards.

Helium Detection System
02. Reasons for Lithium Battery Leak Detection Requirements
A standard lithium-ion battery unit comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a membrane, and electrolyte, arranged within its enclosure. Given lithium metal’s high reactivity, its processing, storage, and usage demand stringent environmental care. Leakage of electrolyte from a battery due to poor sealing prompts vigorous reactions in humid settings, posing grave risks to both the environment and individuals, while also impairing equipment longevity.
Hence, ensuring impeccable assembly and sealing is imperative, including robust leak testing for lithium batteries. Depending on the production stage, one can opt for either helium mass spectrometry or helium leak detection systems.
Employing vacuum conditions and helium mass spectrometry, battery cells, which inherently contain trace helium, can be scrutinized post-welding. This approach validates cell seal integrity, facilitating the identification and exclusion of subpar units.
➤ This automated helium leak detection equipment serves the primary purpose of assessing the effectiveness of sealing nail welding on blade cell.
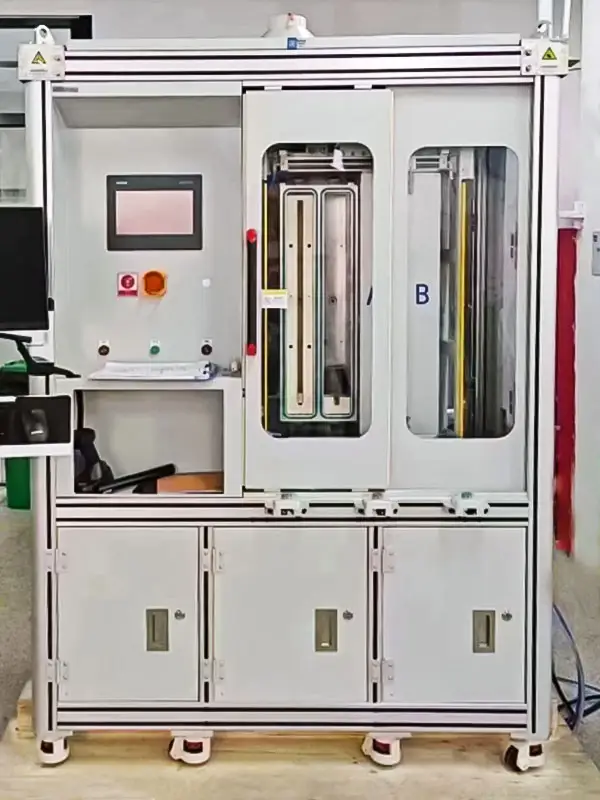

03. The Application Principle of Helium Mass Spectrometer Leak Detector
The helium mass spectrometer leak detector operates on the principles of mass spectrometry, utilizing helium gas as the probing medium for airtightness assessment.
In the testing process, the object under examination is sealed on both sides. Helium gas is introduced on one side, while the other side is linked to the leak detector. This instrument then subjects the detected helium gas to a comprehensive mass spectrometry analysis, enabling the precise calculation of the object’s leak rate.
04. System Workflow
Here’s the detailed operational procedure of the leak detection system for blade batteries:
1. Preparation:
- Turn on the device and supply compressed air and nitrogen via the valves.
- Adjust the pressure to the required level using the pressure-reducing valve.
- Wait for the device to start up and become ready for use.
2. Workpiece Placement:
- The system features one workstation for testing two workpieces simultaneously.
- Scan the code of the first workpiece and position it within Chamber A.
- Scan the code of the second workpiece and place it within Chamber B.
- Sensors in the chambers confirm proper placement.
- The adaptable fixture accommodates different product specifications.
3. Workpiece Clamping:
- Press the start button with both hands to seal the vacuum chamber.
4. Pre-Evacuation and Initial Leak Test:
- Upon sealing the vacuum chamber, the system initiates the evacuation process.
- Successful attainment of the predetermined vacuum level within the specified time indicates a successful pre-evacuation.
- If not achieved, it signals a possible vacuum seal issue, prompting a system halt for operator intervention.
- Once resolved, testing continues.
5. Helium Mass Spectrometry Leak Detection:
- With the lid closed, pre-evacuate Chamber A.
- After successful pre-evacuation, open the leak detection valve.
- The leak detector further evacuates Chamber A to eliminate background gases.
- Conduct a helium mass spectrometry analysis within Chamber A to ascertain leakage rates.
- Record the data from Chamber A before switching to test Chamber B.
- After testing both chambers, evacuate them.
6. Chamber Venting:
- Following leak testing, the system halts and activates the cleaning valve.
- Nitrogen is introduced to vent the vacuum chamber.
7. Workpiece Replacement:
- After chamber venting, the system automatically opens the chamber cover.
- Continue introducing nitrogen to cleanse residual helium.
- At this stage, workpieces can be manually relocated and organized.
This precision-oriented leak detection equipment delivers minimal false-positive results, effectively aligning with production needs of blade batteries. Its adaptability suits contemporary manufacturing lines. The system can interface with PLCs or directly operate external devices (such as relays or solenoids), accommodating varying product testing requisites.
Coolink, a TOP 3 Global HVAC Vacuum Pump Manufacturer & Quality Industrial Vacuum Pump Supplier from China